Why is the UV Index So HIGH in Australia? Factors Affecting UV Rays
Australia experiences some of the highest UV index levels in the world, often reaching extreme ranges, especially during summer. Why is the UV index so high in Australia? Keep reading this post to understand Australia's weather features and take protective actions from harmful sun exposure.
Reasons why the UV index is so high in Australia
- What is the UV Index?
- Why is the UV Index So High in Australia?
- Geographical location
- Clear atmospheric conditions
- The influence of ozone depletion over Antarctica
- Health Effects of UV Radiation
- Skin cancer
- Premature aging and other skin damage
- Cataracts and other eye damage
- Immune system suppression
- How to Protect Yourself from UV Radiation?
What is the UV Index?
UV index is a standard international measurement of the UV radiation from the sun.
Because our eyes can not see UV rays, the UV index is an extremely useful parameter.
Knowing “what is the UV index right now” helps us plan outdoor activities as well as take proper precautions.

UV index definition
The UV index ranges from 0 (low) to 11+ (extreme). According to the Bureau of Meteorology, each point on the Index scale corresponds to 25 milliwatts/square metre UV radiation.
When the UV Index reaches 3 (Moderate) or above, protective actions, such as using a high-protection broad-spectrum sunscreen, are necessary.
Why is the UV Index So High in Australia?
According to The Conversation by Cancer Council WA Education and Research Director Terry Slevin and QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute’s David Whiteman, the high UV index in Australia comes down to geography.
However, going deeper to find out the reasons, we realize that the 3 main factors contribute to Australia’s high UV radiation: geography, clear atmosphere, and ozone depletion over Antarctica.
Geographical location
In fact, the nearer you are to the equator, the higher the UV index is. Thus, sunlight in Australia is often stronger than that in other countries.
Moreover, Australia experiences higher UV levels primarily because of the Southern Hemisphere summer.
During the summer, our planet tilts closer to the Sun, about 5 million kilometers nearer.
At that time, Australia is pointing at the Sun and is exposed to the strongest source of radiation.
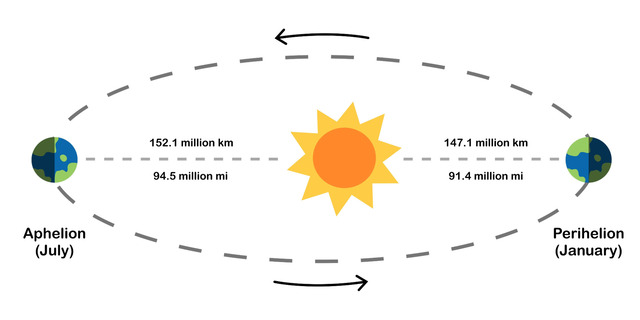
In summer, Australia is closer to the Sun
That said, the country nearer to the Sun than Europe is during its own summer, increasing solar UV intensity by about 7%.
When combined with Australia's typically clearer skies, this leads to Australians experiencing up to 15% more ultraviolet radiation compared to Europeans.
Clear atmospheric conditions
Australia’s typically clear and dry atmospheric conditions contribute significantly to its high UV index.
With fewer clouds, less pollution, and lower humidity compared to many other regions, there is minimal obstruction to sunlight.
This means more ultraviolet (UV) radiation reaches the ground without being scattered or absorbed by particles in the air.
As a result, Australians are exposed to stronger and more direct UV rays, especially during the summer months when the Sun is already more intense due to the Earth's position in its orbit.

Clear atmospheric conditions contribute significantly to its high UV index
The influence of ozone depletion over Antarctica
Australia experiences high UV index levels partly due to its proximity to the ozone hole that forms over Antarctica each year.
The ozone layer, located 10 to 30 kilometers above Earth, plays a crucial role in blocking harmful UV radiation from the sun.
Although the Antarctic ozone hole does not directly extend over populated areas like Australia, its presence nearby contributes to higher UV exposure in the region, especially during the Southern Hemisphere's summer.
In the 1970s, scientists raised concerns about human-caused ozone depletion from chemicals like CFCs.
Thanks to global action through the Montreal Protocol in the late 1980s, the ozone layer has been gradually healing.
Still, Australia’s geographic location and naturally clear skies continue to expose it to intense UV radiation, making UV protection especially important.

The Antarctic ozone hole affects Australia’s UV radiation
Health Effects of UV Radiation
The high UV radiation leads to many potential health problems. Understanding these risks and taking proper precautions will help you enjoy a perfect summer.
Skin cancer
Australia has a high incidence of skin cancer, with about two in three Australians expected to be diagnosed with some form of skin cancer in their lifetime.
There are about 2000 Australians death due to skin cancer each year.
Non-melanoma skin cancer is the most common type diagnosed, accounting for over 1 million treatments annually.
Exposure to UV rays without protective methods is one of the most common risk factors for skin cancer.

Skin cancer in Australia
Premature aging and other skin damage
Prolonged UV exposure can lead to skin disorders like actinic keratoses and premature aging.
Actinic keratoses are rough, reddish growths on sun-exposed areas such as the face, hands, and neck, and may increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
UV radiation also accelerates skin aging, causing thick, wrinkled, and leathery skin. These effects are often mistaken for natural aging.
However, up to 90% of visible skin aging is caused by the sun and can largely be prevented with proper UV protection.

Premature skin aging
Cataracts and other eye damage
UV radiation can cause serious eye conditions, including cataracts.
It also contributes to other eye issues such as pterygium, macular degeneration, and skin cancer around the eyes.
While cataracts are treatable with surgery, they still affect millions and carry high medical costs.
Proper eye protection, such as sunglasses or lenses with 99–100% UV protection, can help prevent this damage.

The sunlight can cause cataracts and other eye problems
Immune system suppression
Scientists concluded that excessive UV radiation may impair the immune system and the skin's natural defenses.
For example, the skin generally defends against strange invaders such as tumors and infections.
Overexposure to UV radiation, however, can impair the immune system, diminishing the skin's ability to protect itself from harmful invaders.
Overexposure to UV can affect the immune system suppression
How to Protect Yourself from UV Radiation?
Infants and children are easily vulnerable to UV rays, but everyone should be careful.
Overexposure to the sun can lead to the development of skin cancer in later life.
Therefore, keep in mind these simple safety tips below to protect yourself and your loved ones from UV radiation:
-
Wear protective clothes and a broad-brimmed hat. Also, wearing sunglasses with 100% UV protection is necessary.
-
Apply sunscreen liberally, at least 15 minutes before going out in the sun.
-
Select a sunscreen with at least 30 SPF or higher
-
Use a lip balm (SPF 30 or higher) to protect your lips
-
Reapply sunscreen if you have been swimming or perspiring heavily.
-
Sit in the shade and avoid extended exposure from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.
-
Keep babies and youngsters out of the sun during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.). Seek trees and other naturally shaded locations where youngsters can play.
-
If you are unable to keep your youngster out of the sun, ensure that their skin and eyes are protected. Applying sunscreen and wearing sunglasses, and, wide-brimmed hat is essential.

Select a sunscreen with at least 30 SPF
Conclusion
Why is the UV index so high in Australia? There are 3 main reasons: geographical location, clear atmospheric conditions, and the ozone hole in Antarctica. Through this post, hope you catch the necessary information and take proper precautions to protect yourself and your loved ones.




0 Comment
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *